The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Empty Capsules for Your Product
When it comes to choosing a capsule type for your product, manufacturers fortunately have several options. Deciding on the correct capsule type can give your business the edge it needs to be successful, and there are several factors to be taken into consideration. There are many benefits when you make an informed choice regarding the kind of capsules to use when manufacturing, with the potential to improve your product’s quality, increase customer satisfaction, and comply with regulatory standards.
Understanding Capsule Types
The differences in capsules usually pertain to the material of which it is made, like those derived from gelatin and plant-based sources; there are even capsules that can be sprayed with a special coating to aid in the body absorbing nutrients. Each capsule type has its own characteristics and advantages in the encapsulation of a product formulation.
Gelatin
Derived from animal sources, like bovine and porcine collagen from bones, cartilage, and skin, gelatin is a flavorless, clear substance that can be used to construct empty capsules. Hard gelatin capsules are suitable for dry, powdered, or pelletized formulations. On the other hand, soft gelatin capsules are used to contain liquids, oils, or semi-solid formulations.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective: Gelatin capsules are generally less expensive to manufacture compared to other capsule types, making them an ideal choice for small businesses and manufacturers looking to minimize production costs.
- Easy to Fill: Gelatin’s stability makes these capsules easy to fill with various substances using both manual capsule fillers and automatic capsule filling machines.
- Widely Available: Due to their popularity and long history of use, gelatin capsules are readily available in a wide range of sizes and colors. They can also be manufactured at a high speed, making your production process more efficient.

Common Applications and Industries
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Gelatin capsules are used extensively for encapsulating prescription and over-the-counter medications. With the ability to mask unpalatable tastes and unpleasant odors, they are ideal for oral medications.
- Nutraceutical Industry: Vitamins, dietary supplements, and herbal products are often encapsulated in gelatin capsules. Because they are easy to swallow in comparison to other solid dose forms, they can enhance the consumer experience.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Some food products, like fish oil or other dietary supplements, are encapsulated in gelatin to improve palatability and the precision of the dosage.
- Cosmetic Industry: Beauty supplements, or cosmeceuticals, are often found in gelatin capsules for skin, hair, and nail health.There is an increasing demand for easy-to-consume beauty solutions like these.
Vegetarian Capsules
An alternative to gelatin capsules, vegetarian capsules are made from plant-derived materials such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) or Pullulan. These materials come from cellulose and other natural sources, making them appropriate for consumers with dietary restrictions or preferences. Vegetarian capsules are available in hard form, like hard gelatin capsules, and are designed to encapsulate dry or powdered substances.
Advantages
- Suitable for Vegetarians and Vegans: Since they are made from plant substances, vegetarian capsules cater to the growing market of vegetarian and vegan consumers.
- Allergen-Free: Vegetarian capsules are free from common allergens, making them a safe choice for consumers with food sensitivities or allergies.
- Stable and Resistant: These capsules’ stability allows them to resist environmental conditions like humidity and temperature, helping maintain the integrity of the encapsulated product.
- Kosher/Halal Certified: Many vegetarian capsules are made to meet Kosher/Halal certification standards, expanding their appeal to a broader consumer base.
Common Applications and Industries
- Nutraceutical Industry: Vegetarian capsules are widely used for dietary supplements, vitamins, and herbal products, particularly those marketed to health-conscious consumers.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: While less common than gelatin capsules, vegetarian capsules are still used for certain medications, especially for those targeting specific consumer groups or requiring allergen-free formulations.
- Sports Nutrition: Supplements such as protein powders, amino acids, and pre-workout formulas are often encapsulated in vegetarian capsules for athletes and fitness enthusiasts who prefer plant-based products.
- Beauty and Wellness: Nutritional supplements for improving skin, hair, and nail health are frequently found in vegetarian capsules, offering an animal-free option that resonates with a large market segment of vegetarian/vegan consumers.
Enteric-Coated Capsules
Enteric-coated capsules are designed with a special coating that prevents them from dissolving in the acidic environment of the stomach. Instead, during digestion they pass through to the intestines, where the coating and capsule dissolves and the contents are released. This targeted release mechanism is particularly useful for medications and supplements that can be damaged by stomach acid or that can cause irritation to the stomach lining.
Advantages
- Protection from Stomach Acid: The enteric coating protects sensitive ingredients from being degraded by stomach acid, ensuring that they reach the intestines and are absorbed by them.
- Targeted Release: By dissolving in the intestines, enteric-coated capsules provide targeted delivery of active ingredients, which enhances their efficacy.
- Reduced Gastric Irritation: Ingredients that may cause irritation or discomfort when released in the stomach are better tolerated when delivered directly to the intestines.
- Enhanced Bioavailability: For some materials, bypassing the stomach can improve absorption rates and bioavailability.
Common Applications and Industries
- Pharmaceutical Industry: These capsules are mostly used for medications that can be negatively affected by stomach acid, such as probiotics and enzyme supplements. They are also used for medicines that are intended to act in the intestines.
- Nutraceutical Industry: Some dietary supplements, like fish oil, are helped by the enteric coating because the active ingredients are not destroyed by stomach acid. This enables them to release their beneficial effects in the intestines.
- Veterinary Medicine: Similar to human applications, enteric-coated capsules are used in veterinary medicine to protect sensitive ingredients and ensure targeted delivery in the digestive systems of animals.
- Gastroenterology: Treatments for gastrointestinal conditions, such as inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, often use enteric-coated capsules to deliver medication directly to the site of inflammation in the intestines.
For a concise comparison of the different types of capsules, please refer to the table below:
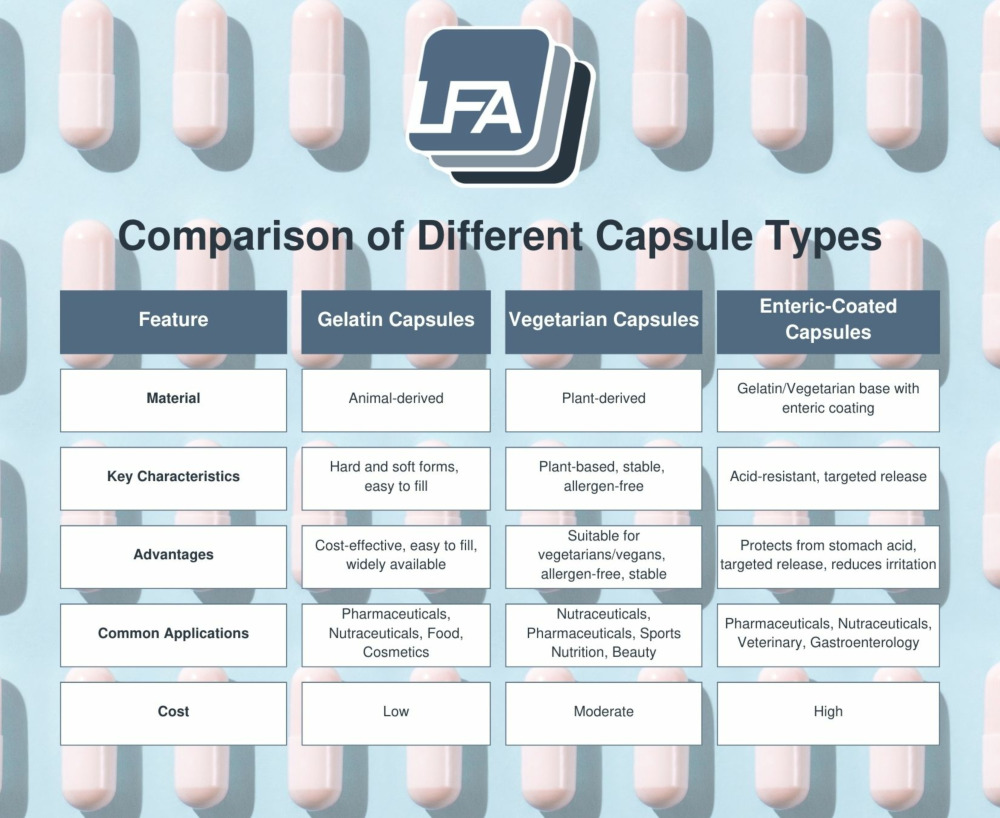
Practical Factors in Choosing Capsule Types
Selecting the right capsule type goes beyond considering their basic characteristics. Practical factors such as compatibility with fillers, the manufacturing and filling process, and storage and shelf life also play important roles in ensuring product quality and production efficiency.
Matching Capsule Types with Different Fillers

Choosing the right capsule type involves ensuring compatibility with the filler material to maintain product quality and efficacy. Here is how to match capsule types with various kinds of fillers:
- Powders: Both gelatin and vegetarian capsules can work with powdered formulations. To avoid clumping and ensure consistent filling, ensure the powder has good flow properties.
- Liquids: Soft gelatin capsules are usually used for liquids and oils, while vegetarian capsules made out of HPMC can be used for non-aqueous liquids. Enteric-coated capsules can be used for liquid contents that need to bypass the stomach.
- Granules: Gelatin and vegetarian capsules are both suitable for working with granules. Making sure the granules are all uniform in size helps with consistent fill weights in the finished product.
- Semi-Solids: Soft gelatin capsules are ideal for semi-solid formulations. HPMC capsules can also be used if the material is non-aqueous.
Avoiding Common Compatibility Issues
In your search for capsules, it is equally important to learn about circumstances that will lead to manufacturing errors during capsule filling.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Gelatin capsules tend to absorb moisture, which can affect both the capsule and the fill formulation. HPMC capsules resist moisture better in comparison.
- pH Sensitivity: Certain formulations can interact with the capsule material based on their pH level. For acidic or basic substances, enteric-coated capsules or specially designed vegetarian capsules might be necessary.
- Solubility Issues: Another thing to consider is that the formulation does not dissolve or degrade the capsule itself. Aqueous liquids are not suited for standard gelatin capsules but can be used in some vegetarian capsules.
Storage and Shelf Life
Like with any product, the environmental conditions in which empty and filled capsules are stored must always be taken into account. To prevent them from degrading, here are some best practices to follow:
- Temperature Control: Storage environments should be cool and dry, with a temperature ranging between 15°C and 25°C (59°F to 77°F).
- Humidity Control: Relative humidity levels should be between 35% and 65%. The moisture in excess humidity can cause gelatin capsules to stick together or become brittle.
- Light Protection: Capsules should be stored away from light, which can degrade both gelatin and vegetarian capsules over time.
Understanding these practical factors can ensure the compatibility, quality, and efficacy of your capsules, resulting in efficient manufacturing processes and high-quality end products. This not only helps to maintain product integrity and consumer happiness, but it also optimizes operational costs and decreases the possibility of production problems.
Cost Considerations in Selecting Capsules
When choosing capsules, quality and cost must be balanced to ensure a cost-effective solution that won’t compromise the state of the finished product. High-quality capsules are less likely to cause production problems; it is worth considering the long-term costs with capsules that might have a higher upfront price (such as Pullulan or enteric-coated capsules) but could save money in the long run by reducing downtime and wasted product. You can also align your capsule choice with the positioning of your product. So, for a premium product, investing in higher quality products may be the best decision.

Determining the cost-effectiveness of different capsule types also involves calculating the direct and indirect costs. Here is a list of the different types of costs associated with manufacturing products with capsules:
- Direct Costs such as the price per capsule, shipping and handling pricing, and, if applicable, any additional costs for storing capsules.
- Production Costs like capsules with faster filling times, their compatibility with your capsule filling machinery, and the integrity of the capsule’s composition (to avoid potential incompatibility defects).
- Indirect Costs such as product returns, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance.
By looking into direct and indirect costs, as well as determining the long-term benefits, you can choose the most cost-effective capsule type for your product. This will help you maintain high product quality while managing your production budget effectively.
Selecting the right type of capsule for your product requires a careful examination of various factors to ensure optimal production. Options like gelatin, vegetarian, and enteric-coated capsules each offer advantages for specific market demands and consumer preferences. By addressing facets such as capsule material, practical factors, and cost-efficiency, you can maximize production, minimize issues, and deliver high-quality products that meet and exceed consumer expectations.
Ready to optimize your capsule filling process and ensure the highest quality for your products? Contact LFA Machines today! Our expert team is here to assist you with selecting the perfect capsules, providing state-of-the-art filling machines, and offering the best support to help your business thrive.